.jpg)
Choose to read by topic:
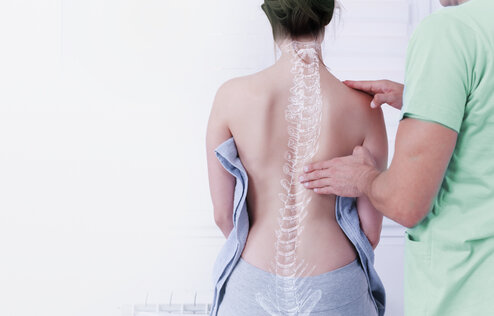
What is Herniated Disc
A herniated disk is a condition most often the result of a gradual, aging-related wear and tear called disk degeneration. This causes pressure on the nerves that exit in the spinal cavity. When this part of the bone presses on the nerves, there is pain that spreads to the top of the leg. Herniation may occur from the back or waist down to the leg, often in a sitting or forward bent position, where the disks are most stressed. The disease is more common in working age.
Herniated disc in neck
The neck consists 7 bones called the cervical vertebra. Between each piece is an intervertebral disk, and between the bones are tendons and muscles. Inside the clavicle are the internal parts of the nervous system, the spinal cord and nerves. In addition, the muscles around the collarbone can move through interconnected joints and bend, tilt, twist and turn the head. If the neck is moved a lot or abused, this can lead to neck pain. However, if more severe neck pain occurs along with neck pain in the arms, it may be caused by a herniated disk that is overlying the nerves in the neck.
Herniated disc in back
In between the spine, there is a tissue called an intervertebral disk that runs from the neck to the waist. It provides cushioning and flexibility when moving in different directions. When a disk is missing, the back can be bent, compressed or moved uncomfortably. With repeated exposure, to applications that directly affect the spine over a long period of time. The fibers of the disk tear and are gradually pushed out and reduced until it presses on the nerves behind it.
Herniated Disc Cause
The main cause of a herniated disk is the degeneration of the disk, which directly affects the spine over a long period of time. Such as repetitive bending or heavy lifting, long car rides, regular activities that require bending of the back and neck. Accidents that directly impact the spine, or even deterioration due to age, causing the fibers of the disk to tear and gradually pushed out until it presses on the nerves on your back.
Herniated Disc Symptoms
- Symptoms of herniated disc affects many parts of the body, including:
- Back Symptoms When disks affect the nerves in the lower spine, there is pain in the back, lower lumbar region, hip and often in the legs. However, when the disk overlaps the nerves, it occurs in the cervical spine. The patient then has neck pain and in the arm. - Symptoms in the legs This results in numbness or weakness in the legs.
- Severe neurological disorders, such as abnormal control of urine and feces, etc.
- Difficulty walking, such as poor balance, difficulty walking, stiff legs.
When to See a Doctor?
Although the pain may take some time for the symptoms to subside. There may be symptoms that are warning signs that you should see a doctor immediately, including:
- The pain does not subside within 2-3 days, or the symptoms become so unbearable that they interfere with daily activities (standing, standing, walking)
- Severe pain, sudden, unusual pain
- Pain is not cured for more than 3 years.
- Neck pain in combination with pain in the arms or pain in the back and legs Arms, legs numb or weak.
- Difficulty walking, such as poor balance, difficulty walking. Stiff legs
- There are problems in controlling the defecating and urinating.
Office Syndrome and Herniated Disc
Office Syndrome
Office Syndrome is a muscle pain syndrome and inflammation of the tissues and ligaments These symptoms are most common in people who work in the office for a long time in the same position. Where the body uses the same muscles over and over Causing the muscles to become too tight, causing pain which is found in more than 50% of the symptoms may come in with similar symptoms, such as back pain, neck pain, but more often than others, there may be one of the symptoms that vary greatly, including headache, fatigue, eye strain, pain. Scapula fatigue, numbness of the hand from pinched nerve endings, and stiffness.
Herniated disc
Most back pain and neck pain caused by office syndrome will resolve within a few days after taking the medication. Stop doing activities that cause back pain, neck pain, as well as adjust the working environment. Doing physical therapy to stretch the muscles, exercise and adjust to a correct posture and be aware of what kind of pain warning that you are at risk of having a herniated disc.
- Persistent back pain for more than 3 months or recurring for more than 2 weeks
- Pain in the neck, back, chest, waist, lower back, or the shoulder area connected to the neck by pain in a small way Like an electric shock or pain.
- Back pain radiating from your hips, legs, to the calf or feet.
- Having problems walking, such as poor balance, difficulty walking, and stiff legs.
- Back pain is accompanied by symptoms of severe neurological disorders, such as numbness, weakness, abnormal urination and stool control, etc.
- When coughing, sneezing, or pushing, it becomes even more painful.
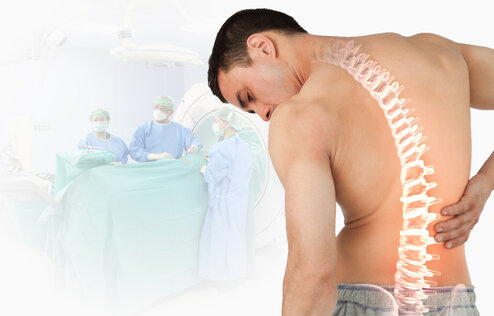
Diagnosis for Herniated Disc
For the diagnosis of herniated discs Doctors will be able to make a diagnosis based on a history and physical examination. Additional tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can quickly detect abnormalities. This allows the doctors determine the extent of the disease and plan further treatment, as he or she can obtain a sharp, detailed image and clearly distinguish between tissues for diseases to be diagnosed more accurately.
Herniated Disc Treatment
Non-Surgical Treatment for Herniated Disc
- Palliative treatment treats early-stage disk herniation with medication, physical therapy, and behavioral changes in daily life.
- Non-surgical treatment of chronic back pain 2.1 Injections into the spinal cavity to relieve chronic back pain Reduces inflammation and swelling of the ganglia caused by herniated disks moving across nerves.
- The use of radiofrequency, also known as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), reduces inflammation of spinal joints and relieves pain in the neck and back by using the heat generated by radiofrequency to abduct the position of bone joints. Pelvic joints or nerves that cause pain.
Surgical Treatment for Herniated Disc
Endoscopic disk surgery for the treatment of herniated disk; the surgery is performed through a high-resolution endoscope by inserting the camera into the spine through a small incision on the skin, which has less pain in the surgical wound, low risk of infection, damage of fine tissue surrounding area is reduced, and the patient recovers faster after surgery. The surgery is generally performed when the following indications are present: Palliative treatment is unsuccessful, there is chronic pain, or there is marked weakness of the arms or legs, or lack of control over excretion, urine or stool.
Herniated Disc Prevention
- Exercise back muscles.
- Avoid sitting in the same position for a long period of time, especially sitting in front of the computer. Also, avoid sitting or maintaining the incorrect postures while doing activities daily.
- Avoid carrying heavy bags or shoulder bag on one side since it causes a body imbalance, resulting in low back pain.
- Exercise with precaution, especially the repetitive exercises such as running, football, basketball, or sports that have to twist or pivot the body: golf, badminton, tennis. It also includes weight lifting.
Conclusion Herniated Disc
In the case of a herniated disk, the nerves are displaced, which in most cases heal themselves through natural mechanisms. Although the pain is severe at first, it usually improves over time. Early admission leads to better treatment results. If you notice any abnormalities, see a spine specialist immediately. Do not endure the pain that occurs, as proper treatment will help you return to a normal daily life.
Online Consultation
Article of Spine Center